The heart is the hardest working muscle in the human body. Located near in the center of the chest, the adult human heart is about the size of a fist. At an average rate of 80 times a minute, the heart beats about 115,000 times in one day, or about 42 million times in a year.
Recognizing the early signs of heart disease and seeking prompt medical attention are important elements in the fight against what is considered the most common and fatal health condition in the United States.

Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias occur when there is a problem with the electrical system that is supposed to regulate a steady heartbeat. With an impaired electrical system, your heart may beat too fast, too slow or irregularly.
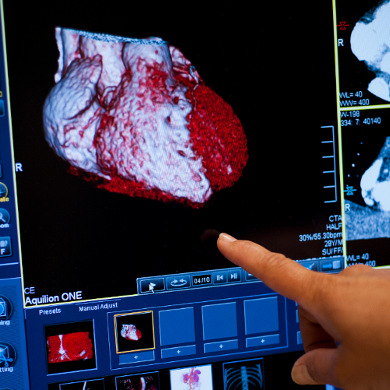
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) occurs when the arteries that bring blood to the heart muscle (coronary arteries) become hardened and narrowed. CAD is the most common type of heart disease and may also be known as coronary heart disease (CHD), heart disease and ischemic heart disease.
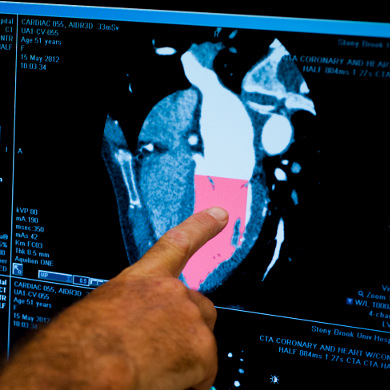
Heart Attack
A heart attack (myocardial infarction) happens when one or more areas of the heart muscle do not get enough oxygen. This happens when blood flow to the heart muscle is blocked. A heart attack can happen to anyone. When you take the time to learn which risk factors apply to you, you can take steps to eliminate or reduce them.
Heart Valve Disease
When heart valves fail to open and close properly, the effects on the heart can be serious, possibly hampering the heart's ability to pump enough blood through the body. Heart valve problems are one cause of heart failure.
Heart Failure
The heart is a muscle that pumps oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body. When you have heart failure, the heart is not able to pump as well as it should. Blood and fluid may back up into the lungs (congestive heart failure), and some parts of the body do not get enough oxygen-rich blood to work normally. These problems lead to the symptoms of heart failure.
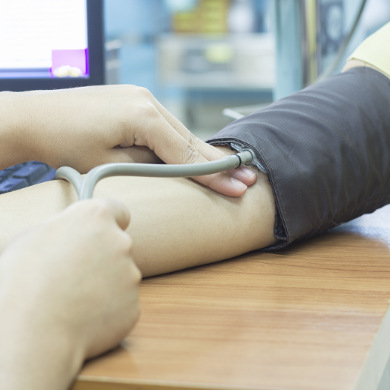
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, directly increases the risk of heart attack and stroke. With high blood pressure, the arteries may have an increased resistance against the flow of blood, causing the heart to pump harder to circulate the blood. Usually, high blood pressure has no signs or symptoms. However, you can identify if you have high blood pressure by checking it yourself or by having it checked regularly by your health care provider.
Vascular Conditions
A vascular disease is a condition that affects the arteries or veins. Most often, vascular disease affects blood flow. This happens when the blood vessels become blocked or weakened, or when the valves in the veins become damaged. Organs and other body structures may be damaged by vascular disease if blood flow is decreased or fully blocked.

Cardiac Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation is a program designed to improve heart recovery, improve your ability to function, and prepare you for future daily activities. People in this program may have had a heart attack or heart surgery. Cardiac rehab can often help you get better at your daily tasks. It may ease your symptoms and give you a sense of well-being.

Pediatric Cardiac Conditions
Diagnosing and treating heart disease in children can be complex and requires clinical care by a pediatric cardiac specialist or other health care professionals. At the Hawaii Pacific Health Heart Centers, our team of physicians and support staff are capable of handling some of the most challenging pediatric heart conditions in the state.
- Anomalous coronary artery
- Aortic stenosis in children
- Arrhythmias in children
- Atrial septal defect (ASD)
- Atrioventricular (AV) canal
- Cardiac catheterization in children
- Coarctation of the aorta (COA)
- Congenital heart disease
- Congenital pulmonary stenosis balloon valvuloplasty
- Echocardiography in children
- Heart failure in children
- Heart transplant in children
- High blood pressure in children and adolescents
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS)
- Pacemaker and implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) insertion
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
- Pericarditis in children
- Pulmonary atresia
- Pulmonary stenosis in children
- Tetralogy of fallot (TOF)
- Total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- Transesophageal echocardiography in children
- Transposition of the great arteries (TGA)
- Tricuspid atresia
- Truncus arteriosus (TA)
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)

Hereditary Arrhythmia Syndrome (HAS)
Genetic variations within our DNA can result in cardiac conditions, such as Hereditary Arrhythmia Syndrome (HAS). In this case, genetic mutations affect the heart cells responsible for the healthy flow of electrical signals that control the heartbeat.
The content available via the website is provided with the understanding that such content is intended solely as a general educational aid. It is not intended as medical or healthcare advice specific to you as the user, or to be used for medical diagnosis or treatment, for any individual problem or concern. It is also not intended as a substitute for professional advice or services from a qualified healthcare provider familiar with you and your condition and/or unique facts. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider regarding any medical condition and before starting any new treatment.